Stoichiometry Tables
Overview
Stoichiometry Tables help you plan and document chemical reactions by automatically calculating reactant quantities and product yields.
When you create a stoichiometry table from a reaction drawing, RSpace extracts the chemical structures and allows you to:
- Specify the limiting reactant
- Define equivalents for each reactant
- Enter (planned) amounts in grams or moles
- Automatically calculate theoretical quantities for all compounds
- Record actual amounts used and automatically calculate yields and excess of products and reagents
This feature streamlines reaction planning and documentation, reducing calculation errors and ensuring accurate record-keeping.
Creating a Stoichiometry Table from a Reaction
To create a stoichiometry table, you first need a reaction drawing in your document.
- Draw or insert a reaction using Ketcher (see Drawing Chemical Structures)
- Select the reaction drawing by clicking on it
- Click the Stoichiometry button in the floating toolbar
- Press Calculate Stoichiometry and define the limiting reagent, reaction equivalents, etc.
- Save the document - stoichiometry tables are only available after saving
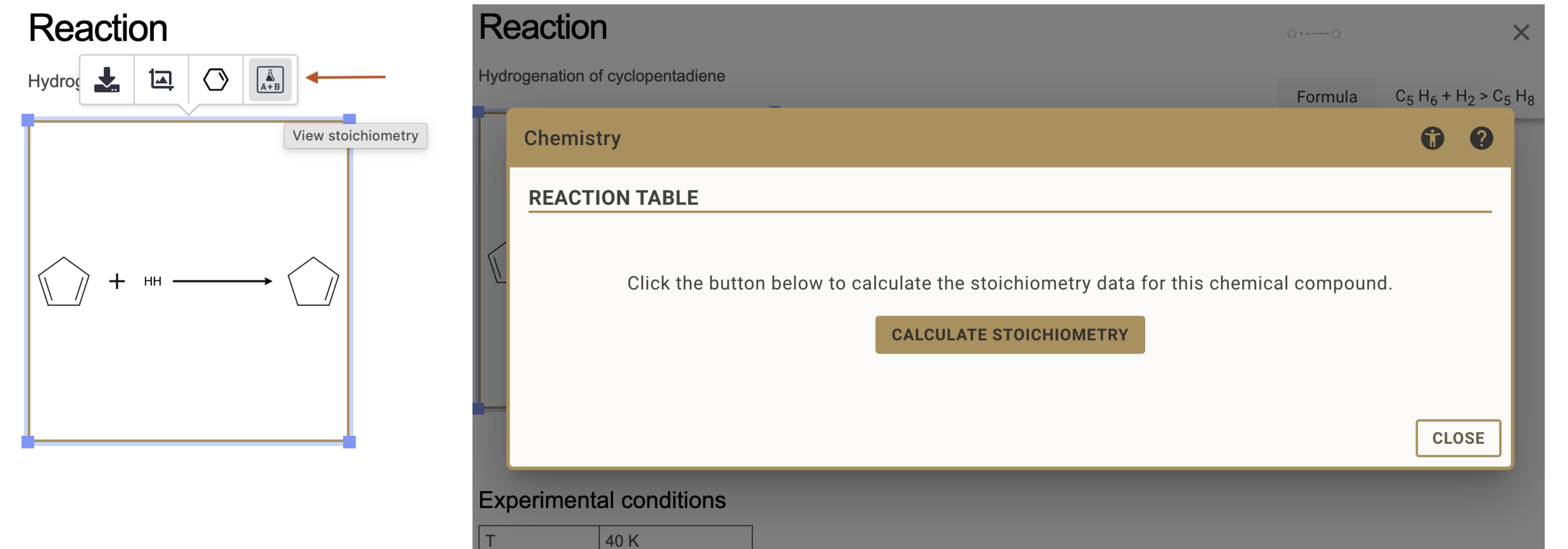
RSpace will automatically create a table with all reactants and products extracted from your reaction drawing.
Understanding the Table Structure
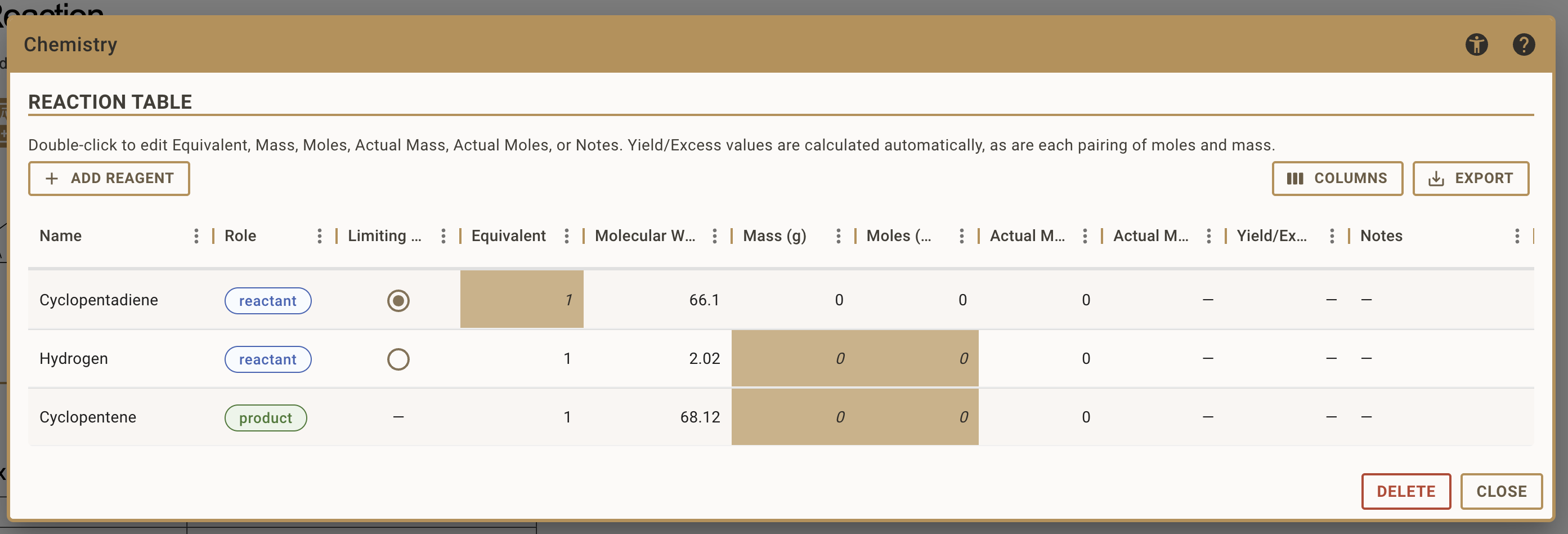
The stoichiometry table contains several columns:
- Name: the name of the reagent
- Role: the role of the reagent, which can be reactant, product or general reagent
- Limiting Reagent: Radio button to designate which reactant is limiting
- Equivalents: Molar ratio relative to the limiting reactant (fixed at 1 for limiting reactant)
- Molecular Weight: Molecular Weight of the compound (g/mol)
- Mass (g): Calculated or entered mass amount
- Moles (mol): Calculated or entered molar amount
- Actual Mass (g): The actual mass you used or obtained
- Actual Moles (mol): The actual molar amount you used or obtained
- Yield/Excess: For products: yield percentage; For reactants: excess amount
- Notes: Any additional context you want to provide
Setting Up Your Reaction
After you initialised the stoichiometry table for the first time, you typically go through the following steps:
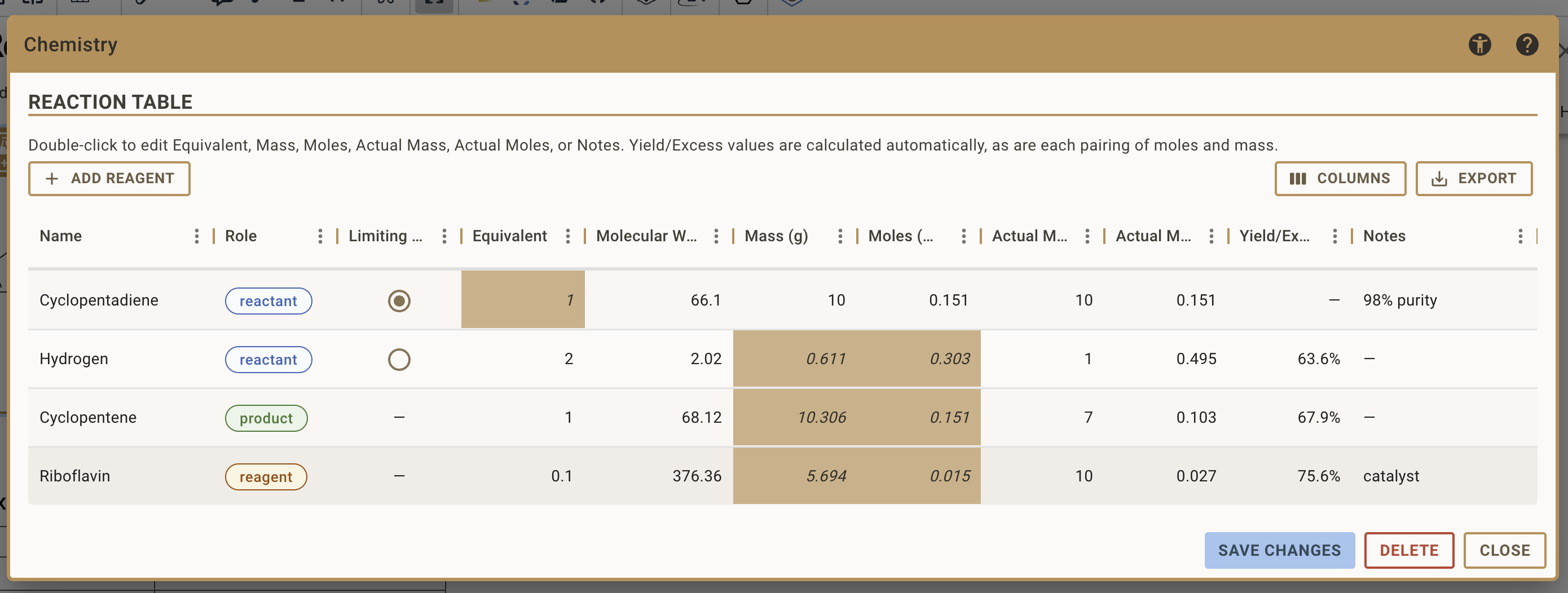
Defining the Limiting Reactant
- Identify which reactant you want to base your stoichiometry calculation on
- Click the radio button in the "Limiting" column for that reactant
- The equivalent for the limiting reactant is automatically fixed at 1.0
- All calculations will be based on the amount you enter for this reactant
Specifying Equivalents
For non-limiting reactants:
- Enter the molar ratio in the Equivalents column
- These values determine how much of each reactant is needed relative to the limiting reactant
Entering Planned Amounts
For your limiting reactant, enter the amount you plan to use:
- Add the planned amounts in either the Moles or Mass field for the limiting reactant. The other is calculated automatically.
- RSpace automatically calculates:
- The corresponding value in the other unit (mass if you entered moles, or moles if you entered mass)
- All other reactants' and products' quantities based on stoichiometry and equivalents
Adding Additional Reagents
To add additional reagents that are not represented in your reaction drawing, such as solvents or catalysts, follow these steps:
- Open the stoichiometry table via the stoichiometry button on the given reaction
- Click "Add Reagent" on the top left of the stoichiometry table
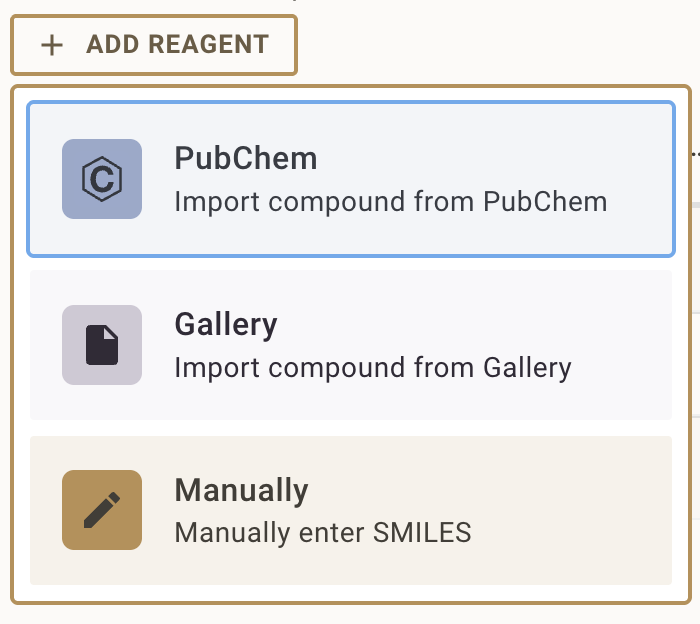
- Choose how to add the compound:
- From PubChem: Search by compound name, CAS number, or SMILES string (see Importing Chemical Structures from external databases)
- From Gallery: Select from previously used compounds in your Chemistry gallery
- Enter SMILES: Manually input a SMILES string
- Enter the equivalent of the newly added reagent to automatically calculate the planned amounts
Recording Actual Amounts and Calculating Yields
After performing your reaction, you can document what you actually used and obtained:
For Reactants:
- In the Actual Moles or Actual Mass column, enter the actual amount you used for each reactant. The table automatically calculates Moles or Mass accordingly.
- The table automatically calculates the Excess in % - showing how much more (or less) you used relative to the expected amount based on the stoichiometry
For Products:
- In the Actual Moles or Actual Mass column, enter the actual amount you obtained
- The table automatically calculates the Yield (%) using the formula:
- Yield (%) = (actual amount / theoretical amount) × 100
This provides immediate feedback on:
- Reaction efficiency and yield
- Which reagents were used in excess or insufficient amounts
- Whether you achieved the expected product quantity
Editing and Updating Stoichiometry Tables
Modifying Values
You can edit the stoichiometry table at any time while editing the document:
- Change equivalents: Click in the Equivalents field and enter a new value
- Update actual amounts: Click in any Actual Moles or Actual Mass field to change values
- Change the limiting reactant: Click a different radio button to designate a new limiting reactant
Calculations update automatically.
Exporting Stoichiometry tables
You can export your reaction table any time as a CSV file by clicking the Export button on the top right of the stoichiometry table.
You can export a document containing a stoichiometry table to XML, HTML or PDF format.