Ascenscia Integration
Overview
Ascenscia is a highly specialized voice assistant mobile application for scientific labs. It is available on App Store (IOS) and Google Play Store (Android. The voice technology solution was created in a modular way to integrate seamlessly with various Laboratory software systems, such as Electronic Lab Notebooks, to enable hands-free voice interactions. Additionally, the software solution acts as a personal assistant for scientists in the labs to mediate their interactions with Electronic Lab Notebook outside of the lab. This enhances the accessibility to data during the experimentation process and the ease of documentation. The phone application has a very intuitive and simple user interface and understands scientific terminologies with 96% accuracy.
Using voice interactions with Electronic Lab Notebook enables scientists to be more productive, capture higher quality of data, and produce higher quality experiments.
Setup and Usage
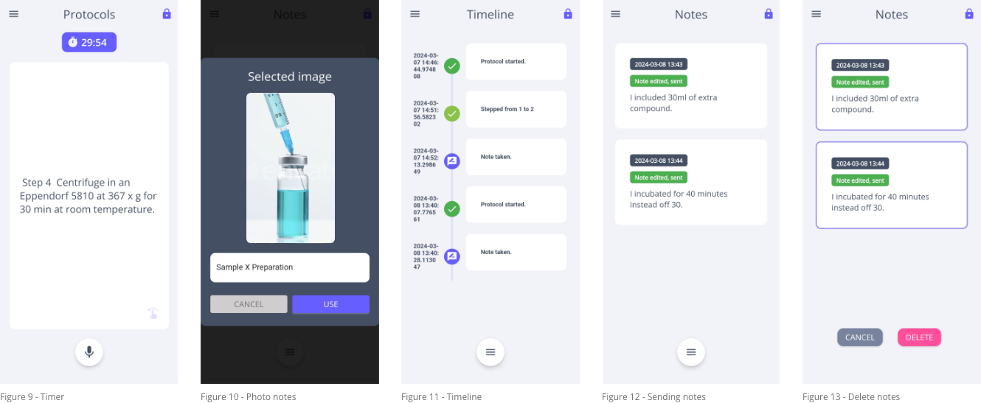
The user can access the ELN system by logging in to RSpace through an API key that they can get from their account on the ELN’s web application (Figure 1).
After a successful login, the user can see all his or her experiments and the ones they have access to in their LabGroup. There is also a search functionality that helps them find experiments quickly (Figure 2).
After selecting an experiment, the application will check how the document is structured. If it uses a Ascenscia Template, it is able to split up the protocol steps and guide the user though the experiment.(Figure 3). If not, the user can still open the experiment and make notes. The notes will be synced to the Data section in the standard RSpace template.
Voice Commands
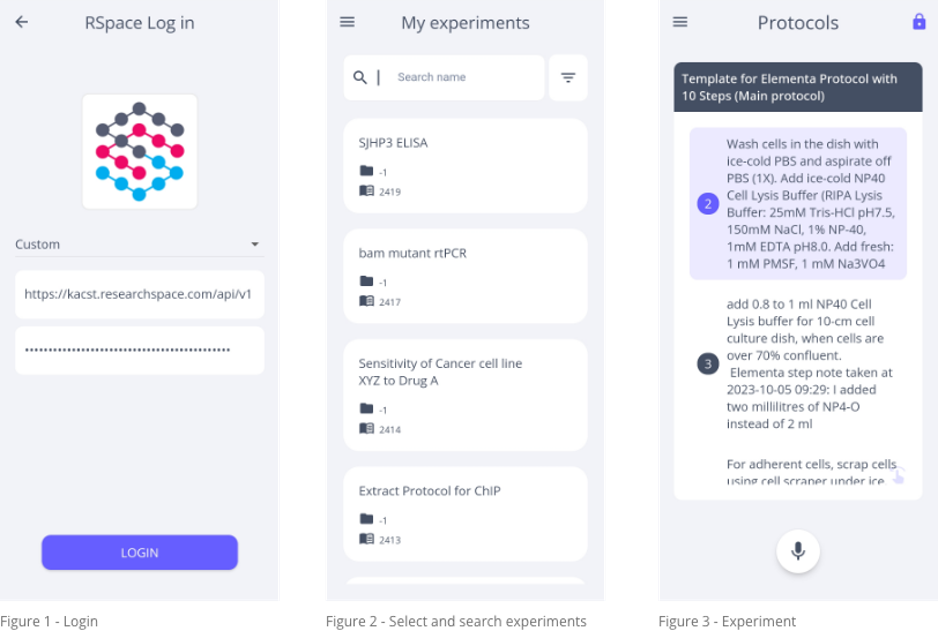
When the experiment is opened, the user will see the protocol steps and start their experiment using simple voice commands. With the voice commands Start Protocol, Next, Previous, Repeat and Jump to step [number] they can navigate their protocol by voice. The steps will be narrated to the user so they can keep their eyes on the experiment and will not lose focus (Figure 4).
During the experiment, the user can make notes with the Make a Note or Make a Step Note voice commands. The voice recordings are saved on device, and when the user opens the note section all the notes will be transcribed. Every note has the original voice recording and can be edited before being synced to RSpace. All the notes can be deleted from the device as well (Figure 5).
If there are samples attached to the protocol steps in RSpace, Ascenscia is able to read them in the application as well. The samples are numbered in the application, these numbers can be used to ask the location of these samples (e.g. Where is sample number 1?) (Figure 6).
If the document is using a Multi-protocol Ascenscia Template, users are also able to switch between protocols within the experiment with the simple UI interface or using the Switch to Protocol voice command (Figure 7).
All the voice commands are listed in the Help Section accessible in the side menu of the experiment view in the application (Figure 8).
Additional Features
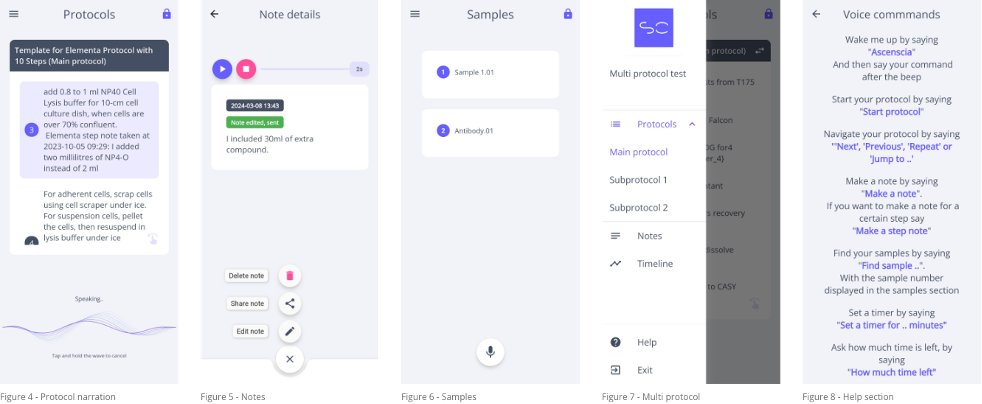
The user can set timers by voice with the Start timer voice command. After the user says the number of minutes the timer starts running. At all times the user can ask for an update with the How much time left voice command or use the Stop timer voice command (Figure 9).
Next to voice/text notes, Ascenscia allows users to make Photo Notes that can be accompanied with a caption (Figure 10).
Voice settings can be set to the user’s satisfaction. These settings include Cut-off time, Sensitivity, Voice Speed and others. This way, Ascenscia can cover a multitude of situations in labs and users (e.g. labs that have loud machines will need a different sensitivity).
All interactions with the application are saved in a timeline on device, that can be shared with others (Figure 11).
After the experiment
If all notes are transcribed and (optional) edited, the user can send the notes with a simple press of a button. The notes will now be sent to the RSpace experiment. All notes have a timestamp for when the note was taken, and Step Notes will go to their respective step in the protocol. Individual notes can also be shared by email, WhatsApp or other apps (Figure 12).
After syncing, the user can safely delete all their notes from the device. As nothing is stored in the cloud, when deleting these notes from the device there is no data left except the data that went to the RSpace experiment (Figure 13).