The PI Role
Overview
RSpace’s PI role is intended to represent the leader of a lab, a course leader, or anybody with responsibility for other people’s work. PIs can create their own content, just as a regular user can, but in addition can:
- Add and remove users from their group
- Alter roles of people within their group
- Organise content that is shared within the group
- View content created by group members. LabGroup members’ work is automatically shared with the PI with "View" permission. Users can manually share data to add "Edit" permission, OR if your server has been configured to do so, PI's can use the option to give themselves "Edit" permission to LabGroups that that they lead.
- Create collaboration groups with other PIs
- View and search the audit trail for work performed by group members
- Export and archive their group’s work
These features are documented in:
- LabGroups
- Collaboration Groups
- Viewing and Organising Shared Group Content
- Examples of Sharing Scenarios and Project Organisation
- Exporting a LabGroup’s Work
- other articles in the PI documentation
- Much of the day-to-day work and most of their powers and permissions can be delegated to LabAdmins (see The Lab Admin Role).
- A LabGroup can only have one primary PI. If your Lab already has, or needs more than one PI, those users will need to be given the "Senior LabAdmin" role. You can have as many Senior LabAdmins in a LabGroup as you need.
Viewing your LabGroup's work
In the Workspace toolbar, select the LabGroup records button. This filters your view to only display the Home folders of users who are members of your LabGroup, and the LabGroup shared folder for any LabGroups you belong to. PIs have permissions to open and view these documents. You can also reach this location by going to the last page of your workspace and navigating to Shared / Labgroups.
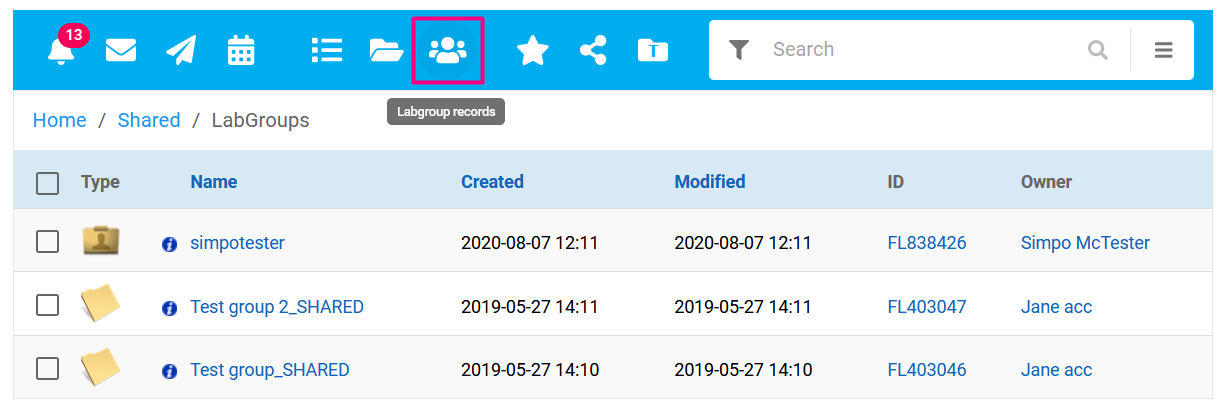
If you regularly want to view the Home folders of a subset of users, you can favorite folders using the checkbox:
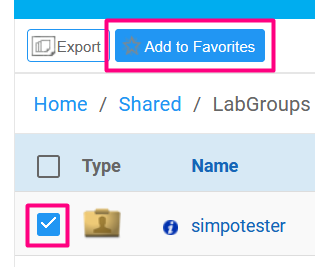
And then use the toolbar's Favorites filter to view them.
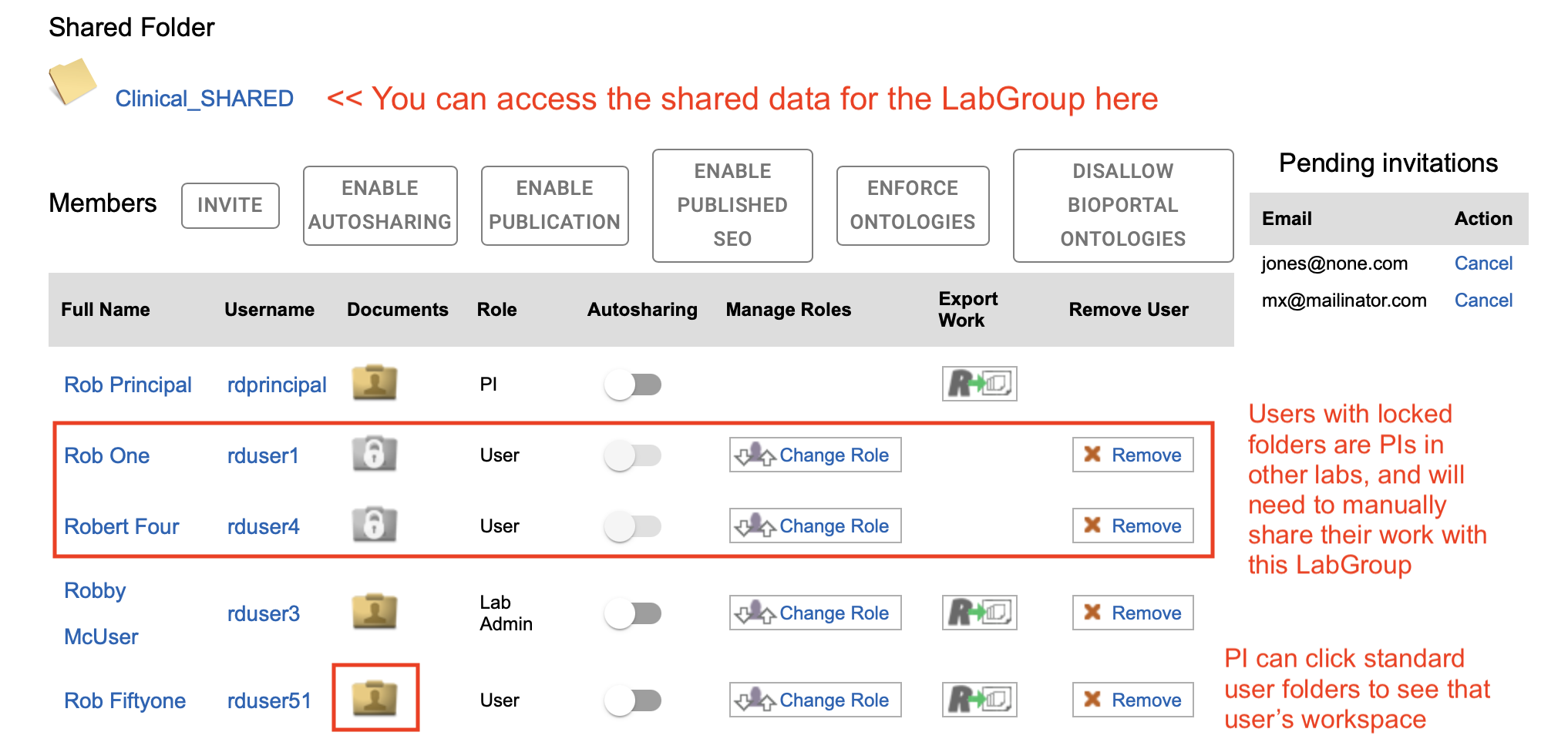
Another way for a PI to access the work of indivuduals in their LabGroup or work shared with the whole LabGroup is to navigate to My RSpace > My LabGroups and then click the folder for shared work or any of the individual user folders to see the workspace for any enabled or disabled LabGroup member. See image below for example of how PI rdprinipal can can see the workspace of rduser51. Note that as a professional courtesy we do not allow one PI to see all the work of another PI by default. Those users' folders show as "locked". A PI can still optionally choose to manually share some or all of thier work if they want to.
In RSpace Community Edition, anyone can designate themselves as a PI but in RSpace Team and Enterprise, PIs are created, revoked and assigned to LabGroups by the System Administrator (sysadmin). The sysadmin can also:
• Change the PI for a given LabGroup
• Adjust the group membership and roles
• Grant PIs the ability to create their own new LabGroups
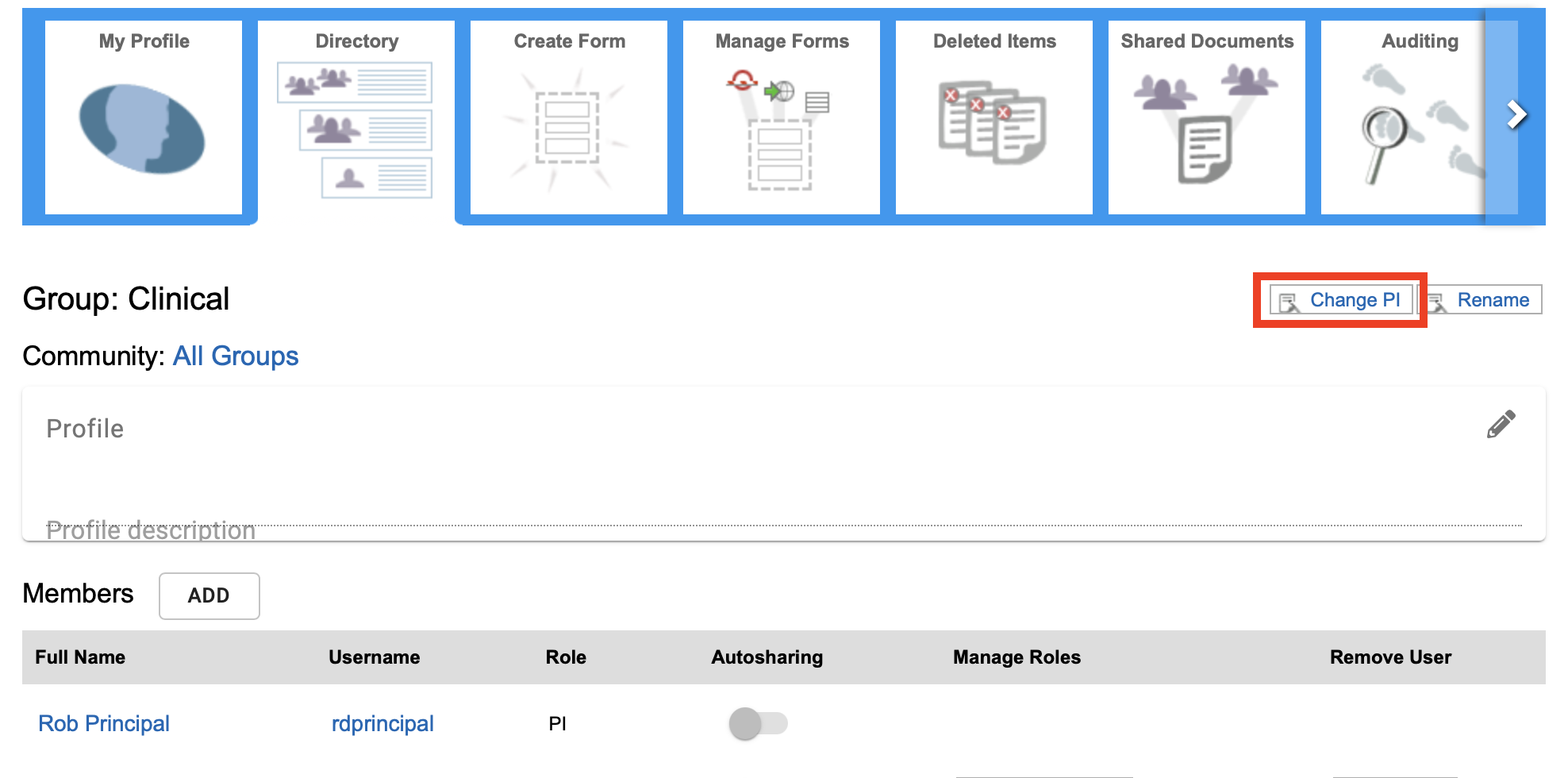
Changing a LabGroup PI
To change the PI within a group, the group must first have at least 2 members with the role of PI. If the group only has one member with the PI role, then that role must first be granted to at least one other memeber before the PI of the group can be changed by the sysadmin using the "change PI" button on the LabGroup page.
Enabling PI Edit access for all work in a LabGroup
If you are a PI and you want to have edit access by default for all data in any LabGroup that you lead, you first need to ask your System Admin to allow that feature using System > Configuration > System Settings > pi_can_edit_all_work_in_labgroup.
Once this has been enabled, the PI can go to My RSpace > My LabGroups, select a LabGroup from the Change Group dropdown, click the edit icon at the top right of the LabGroup page and click the checkbox "PI can edit all work in this LabGroup" then click "SAVE". This will change the PIs default access from read to edit for all work in that labgroup, regardless of whether group members have explicitly shared their work with the LabGroup. As usual, the server audit trail and the document revision history will clearly indicate who has edited each document and when each edit occurred.
